Note: Changes in late 2017 have made the status of CBD very unclear. I personally do not know if CBD is legal in states where marijuana is not legal. Please keep this in mind, according to the DEA the websites selling CBD online are doing so illegally. Be cautious if you purchase these not to take them to places where you might be asked, such as schools or your job. If you or a loved one needs CBD, I encourage you to promote education and to lobby to change the Federal law and legalize all cannabis plants completely nation-wide in order to end this confusion.
some of the information on this page is outdated. Scroll to the bottom of the article for an update.
 As far as I can determine, Cannabidiol (CBD) is legal in all 50 states. If it wasn’t it wouldn’t be sold everywhere in the US and online. In the US, CBD is gaining in popularity especially in the mental health, cancer, chronic diseases, and chronic pain circles.
As far as I can determine, Cannabidiol (CBD) is legal in all 50 states. If it wasn’t it wouldn’t be sold everywhere in the US and online. In the US, CBD is gaining in popularity especially in the mental health, cancer, chronic diseases, and chronic pain circles.
CBD has always been legal in all 50 states. It’s never been scheduled. There is no need to struggle, purchase any illegal herbs, or wait for an Rx from a doctor. CBD products are sold all over the US. Here is a federal finding in the 9th district. The only higher power is the US Supreme court who has not taken this case to overturn.. CBD was never scheduled under the CSA of 1970.
Quote from CNN
“CBD Oil from industrial hemp is already legal in all 50 States because the initial product, hemp, contains no traceable amounts of THC, and therefore is already legal to transport across State lines. Industrial hemp is genetically bred to have high levels of CBD, which is non-psychoactive, and safe for children and the elderly to consume (there is no “high”).”
from: http://ireport.cnn.com/docs/DOC-1251365
Please note: Hemp is not GMO. In fact, most cannbis contained low THC but over the years was bred to become the modern day marijuana high in THC. Hemp is very low in HTC but pretty high on CBD. Selective Breeding (not genetic engineering) with hemp produces strains with even higher CBD content.
The FDA considers hemp and hemp-derived extracts to be food-based products. As such, there are no legal restrictions on their importation, production and consumption in the United States, and in most of the industrialized world. Think of hemp protein, hemp milk, hemp seed oil, hemp clothing, etc.. all legal!
Hemp oil is legal in all 50 states, and in over 40 countries around the world. In Mexico and Brazil, the governments approved RSHO products (by HempMeds, a sister company to Kannaway, using the same CBD oil) for use as medication with a number of medical conditions; in Brazil the government subsidizes this. Here in the US, this is a food, a nutritional supplement, off the counter.
There are millions of hemp oil consumers around the world, and this number is rapidly rising with an increasing number of reports and studies showing a variety of benefits of hemp oil.
While the growing and cultivation of Hemp in the US might still be vilified, luckily CBD-rich, Hemp Stalk, Hemp Bud, and Cannabinoid rich Hemp oil “is legal” in all 50 states.
Since only THC and a few synthetic Cannabinoids are scheduled substances, as long as an imported hemp plant meets the THC threshold, ALL of the Cannabinoids present in it, including the trace amounts of THC, are legal to sell in the Hemp finishing products used in producing nutritional supplements and Hemp foods.
These Hemp products have been legal to sell in the US for some time now, but the growing of Hemp remained illegal until 2014 and early manufacturers of Cannabidiol products were forced to import their Hemp base from overseas. With domestic hemp programs coming online slowly in 2014, and being legally distinct under law from Marijuana via the Farm Bill, producers of High CBD Hemp Oil will now be able to switch from imported base material from Europe and China to higher quality, domestically grown medicinal Hemp strains such as Charlotte’s Web, leading to vast improvements in both potency per dollar spent and overall Cannabinoid profiles.
How is CBD legal, but growing Hemp in the US not legal?
 A derivative of the industrial or commercial hemp plant, CBD Rich Hemp Oil is offering a great legal alternative for those living in non medical marijuana states that would like to try CBD oil but are still waiting for the laws to catch up in their part of the country, as well as folks just seeking highly concentrated sources of Cannabidiol in general. This type of Hemp oil should not be confused with well known nutritional products that have been sold for some time now such as Hemp seed oil, which are sold for their high nutritional value and typically contain very little if any Cannabidiol or other Cannabinoids. These nutritional products are however, sold under the same laws that allow for Hemp based Cannabinoids to be sold legally.
A derivative of the industrial or commercial hemp plant, CBD Rich Hemp Oil is offering a great legal alternative for those living in non medical marijuana states that would like to try CBD oil but are still waiting for the laws to catch up in their part of the country, as well as folks just seeking highly concentrated sources of Cannabidiol in general. This type of Hemp oil should not be confused with well known nutritional products that have been sold for some time now such as Hemp seed oil, which are sold for their high nutritional value and typically contain very little if any Cannabidiol or other Cannabinoids. These nutritional products are however, sold under the same laws that allow for Hemp based Cannabinoids to be sold legally.
CBD content in Hemp oil, when extracted from the proper strains, can be very high as Hemp plants are now the very strains that are being used to breed high CBD levels back into Cannabis after years of selective recreational breeding for high THC values. Well known strains such Charlotte’s Web are hybrids that were selected from crosses with High CBD Hemp varietals and those Hemp genetics are what account for the new High CBD Strains of Marijuana and commercial Hemp that have and are being developed. Industrial and commercial Hemp has been bred over decades to reduce the THC limits beyond .3%, as to meet the international guidelines for industrial hemp certification, but the CBD has remained untouched, whereas in the recreational market, the exact opposite has happened over the last 30 or 40 years of indoor growing. The money has traditionally been in high THC values, and as a result CBD was slowly selected against in favor of high THC .
CBD modulates/diminishes the effects of THC so is not a desired trait for recreational strains of cannabis for the most part, unless in very small concentrations. Strains that approach a 1:1 ratio of THC to CBD have very little if any intoxicating effect and are more suitable for medicinal use where high THC doses can be uncomfortable for some. It is only with the recent surge of interest in Cannabidiol that breeders are getting the financial incentive to work with these previously abandoned hemp strains in order to bring CBD back into the Cannabis genetic pool and develope strains such as Charlotte’s Web, Cannatonic, ACDC and Harlequin, among many other high CBD variants, some of which now have low enough THC levels to qualify for industrial Hemp status. A great breakdown of some of the most well known High CBD strains being used to make Marijuana oil and extracts in Medical Marijuana states today may be found here via Synergy Wellness’s site.
In 2004, the 9th US Circuit Court of Appeals ruled that the naturally occurring Cannabinoids contained in non psychoactive varieties of Cannabis (industrial Hemp) are outside of the regulatory power of the DEA after the DEA attempted to enforce a zero tolerance policy on the trace amounts of THC contained in Hemp products being sold at the time, such as nutritional Hemp seed oil. One can view these trace amount of THC being very similar to the trace amount of morphine and codeine found within poppy seeds used for baked goods. This zero tolerance policy was challenged by the HIA (Hemp Industries Association) who won the ruling in 2004, which was subsequently left unchallenged by the Bush administration and DEA. Industrial Hemp is defined internationally as having .3% THC or less by dry weight, so that has become a defining line between what is legally considered Hemp and what is considered “Marijuana” under U.S. law after the 9th circuit court of appeals ruling that placed the Cannabinoids contained within Hemp into a separate category than those within strains of Marijuana with higher than .3% THC content.
If CBD is derived from Marijuana, it is illegal as are all constituents of the plant. When derived from imported commercial hemp, CBD is legal as the Cannabinoids contained in non-psychoactive strains of Cannabis are exempt from regulation in the US and around 40 other countries when used in Hemp finishing products. Some countries do in fact schedule Cannabidiol, such as Canada, where CBD is listed as a Schedule 2 substance.
Legal status of Cannabidiol can been seen on the wiki page here.
Strains such as Charlotte’s Web, that started out being classified as “marijuana” strains, have now been able to be reclassified as Hemp strains, due to the meeting of the 0.3% THC threshold.
This is an important designation, as breeders are now breeding Cannabis strains down to acceptable THC levels, while still offering a plant that carries all of the other combinations of naturally occurring Cannabinoids, which provide a synergistic effect when taken together along with the plants given Terpenoid and Flavanoid profiles.
This has tremendous implications for people that do not need high THC levels in their Marijuana oil and extracts as it offers a legal avenue to procure CBD Oil for Sale in all 50 states.
The 2014 Farm Bill took further steps to distinctly define hemp in the U.S. to allow for early pilot farms to develop and the pending Industrial Hemp Act will sever hemp’s connection with marijuana under the Controlled Substances Act once and for all.
Do not confuse Hemp with Marijuana. Marijuana (like hemp) is from the genus cannabis, and does contain CBD (but, it also contains high THC). CBD-rich Hemp has more CBD (and minute amounts of THC, less than 0.3%) that makes hemp products legal to be sold in the US.
Text from a CNN article:
Title: CBD Oil Grown from Industrial Hemp is Already Legal in All 50 States
Due to many States “legalizing” CBD (Cannabidiol) Oil for use in patients, we thought it important to help you understand what the difference is between CBD Oil from marijuana versus CBD Oil grown from industrial hemp. CBD Oil from marijuana is not yet legalized in all 50 States because the initial product made from marijuana plants (genetically bred to be high in levels of THC), has higher THC before the CBD is isolated from the plant. CBD Oil from industrial hemp is already legal in all 50 States because the initial product, hemp, contains no traceable amounts of THC, and therefore is already legal to transport across State lines. Industrial hemp is genetically bred to have high levels of CBD, which is non-psychoactive, and safe for children and the elderly to consume (there is no “high”). Marijuana is different than hemp . Marijuana has high levels of THC, and is not yet legal to grow and consume in all 50 States. Hemp is different, because it is legal to consume products made from hemp in all 50 States, and has been for a long time. When you hear that CBD Oil is becoming “legal” in a State – it means that CBD Oil from THC-high marijuana plants can be consumed. CBD Oil from industrial hemp is already legal to consume, buy, and sell in all 50 States because there’s no traceable amounts of THC in the end products, and instead are rich in the compound CBD. Don’t forget…. be sure to ask these four critical questions when choosing a CBD Oil supplement!
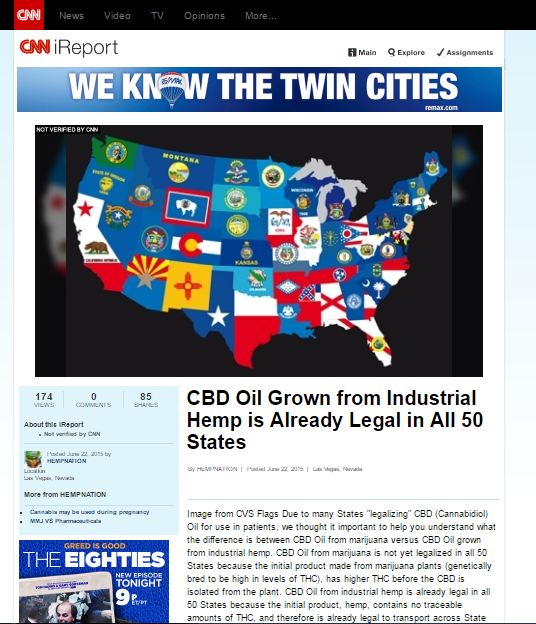
Source: http://ireport.cnn.com/docs/DOC-1251365
 Below I pasted text answering this question from Medical Marijuana Inc, one of the largest and most respected companies in the field of cannabis oils and CBD oil:
Below I pasted text answering this question from Medical Marijuana Inc, one of the largest and most respected companies in the field of cannabis oils and CBD oil:
This seemingly simple question has many people — from mainstream Americans to federal regulators — utterly confused.
Before digging into the details, the bottom line is that cannabidiol is legal, with consideration to its source.
Cannabidiol itself is not specifically listed on the United States Controlled Substances Act, the way THC and marijuana are. At the federal level, the Marihuana Tax Act defines ALL Cannabis sativa as “marihuana” and specifies all the parts of the plant that are prohibited: not surprisingly, that list includes the leaves and the flowers.
However, the politicians who wrote up the definition of “marihuana” included some provisions about what “marihuana” was not. Here’s what they had to say:
“The term ‘marihuana’ means all parts of the plant Cannabis sativa L., whether growing or not; the seeds thereof; the resin extracted from any part of such plant; and every compound, manufacture, salt, derivative, mixture, or preparation of such plant, its seeds, or resins; but shall not include the mature stalks of such plant, fiber produced from such stalks, oil or cake made from the seeds of such plant, any other compound, manufacture, salt, derivative, mixture, or preparation of such mature stalks (except the resin extracted therefrom), fiber, oil, or cake, or the sterilized seed of such plant which is incapable of germination.”
The key words here for us are “mature stalks” and “oil or cake made from the seeds” and “sterilized seeds.” Even though it’s a mouthful, the government draws a clear line in the sand as to what parts of the plant These “not marihuana” parts of hemp are the parts that we use to make our CBD hemp oil products.
But we’re not the only ones. These “not marihuana” parts of cannabis are what all hemp companies use to make their products — from hulled hemp seeds to hemp seed oil to hemp protein [cake made from the seeds] to hemp clothing and hemp concrete [fiber from mature stalks].
And while you can’t grow hemp in the US at the national level yet, importing hemp products — like fabric, rope and oil — has been legal for decades. Remember — the United States imports over half a billion dollars worth of hemp products from overseas every year.
Like many other hemp companies, we too import hemp oil from Europe. This hemp oil, naturally abundant in CBD, is what’s at the core of all our brands and products. It’s not an extract, it’s not part of marijuana; it’s a natural part of legal hemp oil, as inseparable from that oil as vitamin C is from orange juice.
As you can see, it’s a tangled legal web. However, it is encouraging to see more and more attention being paid to CBD by regulators, and we are confident that as they weigh the pros and cons of legality for consumers, businesses, and society, a clear, beneficial legal environment will eventually come to be.
Source: http://medicalmarijuanainc.com/is-cannabidiol-legal/#sthash.OOxny6rV.dpuf
.
From HempMed:
Federal Definition
Finally, the federal government considers some parts of cannabis sativa L. “marihuana” (most obviously, the flowers of the plant) and excludes other parts from that definition (like the mature stalks, fiber, sterilized seeds and anything produced from those parts), which are generally called “hemp,” “industrial hemp” or “commercial hemp.” These distinctions between marijuana and hemp are why hemp milk, hemp protein, hemp oil, hemp seeds, and other consumer products made from hemp are freely available for purchase throughout the United States. We as a nation import over half a billion dollars of hemp products annually thanks to this important distinction.
Source: https://hempmedspx.com/the_faq/
Update: From Medical Marijuana Inc MJNA, the absolute CBD leader in the country and the parent company of Kannaway (from late 2016) :
Medical Marijuana, Inc. CEO Clarifies Company Position Following DEA Announcement
On Wednesday, December 14th, the DEA included a section (21 CFR Part 1308) in the Federal Register changing the language in its current drug code. In response to the recent DEA change in the Federal Register, Medical Marijuana, Inc. CEO Dr. Stuart Titus released the following statement.
“Medical Marijuana, Inc. is pleased to announce that the DEA Federal Registry amendment to create a new code for ‘marijuana extracts,’ in no way affects the Company’s hemp oil, containing naturally occurring cannabinoids, including CBD, or its operations,” Dr. Titus said.
Titus went on in the release to say, “In the past, the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals has
conclusively held thxat hemp products, such as those marketed by the Company, which are
derived from the part of the Cannabis plant which is exempt from the Controlled Substances Act, is legal for import from Europe. In the Ninth Circuit case that served to uphold the legality of the Company’s products, the Court struck rules that had been promulgated by the DEA that would have made the Company’s products a scheduled substance and the Court permanently enjoined the DEA from enforcing the stricken rules. There has been no superseding ruling since the Ninth Circuit’s decision.”
“Therefore, the Company’s products continue to be legal and are not controlled substances. Accordingly, the legality of Medical Marijuana, Inc.’s products remains unchanged in light of this new Federal Registry. Further, our Company considers the development a major market opportunity, as we have analyzed and followed the chain of custody of our products from inception to ensure that they are derived from the exempt part of the Cannabis plant and are therefore not controlled substances,” Titus concluded in the released statement.
Source: http://www.medicalmarijuanainc.com/medical-marijuana-inc-ceo-clarifies-company-position-following-dea-announcement/
Dr. Titus explaining:
Update: Dec 2017
The DEA reiterated its position as of July 2017 in the following statement provided to The Cannabist:
DEA Statement on CBD, Hemp and “Farm Bill”
“Media attention has focused on a derivate of marijuana that many refer to as ‘Charlotte’s Web’ or ‘CBD oil.’ At present, this material is being illegally produced and marketed in the United States in violation of two federal laws: The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) and the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FDCA). Because it is illicitly produced by clandestine manufacturers, its actual content is uncertain and will vary depending on the source of the material. However, it is generally believed that the material is an extract of a variety of the marijuana plant that has a very high ratio of cannabidiol (CBD) to tetrahydrocannabinols (THC). Because this extract is a derivative of marijuana, it falls within the definition of marijuana under federal law. Accordingly, it is a Schedule I controlled substance under the CSA.
“As with all controlled substances, it is illegal under the CSA to produce or distribute ‘Charlotte’s Web’/CBD oil (or any other marijuana derivative) except by persons who are registered with DEA to do so. Because ‘Charlotte’s Web’/CBD oil is not an FDA-approved drug:
- It is a schedule I controlled substance under the CSA;
- It is unlawful under the FDCA for any practitioner to provide the material to human beings under the guise of ‘research’ without first submitting an Investigational New Drug (IND) application to the FDA;
- The CSA requires that any person seeking to conduct research with the material obtain a registration with DEA authorizing such research;
- The CSA further requires that the researcher obtain the schedule I material from a legally authorized producer.
“All of these requirements (submission of the IND to FDA, obtaining a DEA research registration, and obtaining the material from a lawful source) are essential to protecting human research subjects from the potential dangers of using an experimental drug and are essential to the scientific integrity of the research. Because ‘Charlotte’s Web’ is reportedly being administered to pediatric research subjects, the potential dangers are even more pronounced, making compliance with the FDA IND requirement even more crucial.
“It is important to correct a misconception that some have about the effect of the Agricultural Act of 2014 (which some refer to as the ‘farm bill’) on the legal status of ‘Charlotte’s Web’/CBD oil. Section 7606 of the Agricultural Act of 2014 authorizes institutions of higher education (e.g., universities) and state Departments of Agriculture to grow and cultivate ‘industrial hemp’ (defined under the Act as marijuana with a THC content of 0.3 percent or less) for agricultural research purposes where permitted under state law. However, the Agricultural Act of 2014 does not permit such entities, or anyone else, to produce non-FDA-approved drug products made from cannabis. Thus, the CSA and FDCA restrictions mentioned above remain in effect with respect to the production of ‘Charlotte’s Web’/CBD oil for human consumption.”
Also visit for more info:
https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/schedules/marijuana/m_extract_7350.html
Quote:
Because recent public inquiries that DEA has received following the publication of the Final Rule suggest there may be some misunderstanding about the source of cannabinoids in the cannabis plant, we also note the following botanical considerations. As the scientific literature indicates, cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinols (THC), cannabinols (CBN) and cannabidiols (CBD), are found in the parts of the cannabis plant that fall within the CSA definition of marijuana, such as the flowering tops, resin, and leaves.2 According to the scientific literature, cannabinoids are not found in the parts of the cannabis plant that are excluded from the CSA definition of marijuana, except for trace amounts (typically, only parts per million)3 that may be found where small quantities of resin adhere to the surface of seeds and mature stalk.4 Thus, based on the scientific literature, it is not practical to produce extracts that contain more than trace amounts of cannabinoids using only the parts of the cannabis plant that are excluded from the CSA definition of marijuana, such as oil from the seeds. The industrial processes used to clean cannabis seeds and produce seed oil would likely further diminish any trace amounts of cannabinoids that end up in the finished product. However, as indicated above, if a product, such as oil from cannabis seeds, consisted solely of parts of the cannabis plant excluded from the CSA definition of marijuana, such product would not be included in the new drug code (7350) or in the drug code for marijuana (7360), even if it contained trace amounts of cannabinoids.5
Update January 2018:
From: https://www.leafly.com/news/politics/cbd-oil-legal-depends-ask
Quote:
Cannabidiol, or CBD, is just one of over a hundred cannabinoid compounds found in cannabis. THC is the cannabinoid most folks are after when looking for a high. In contrast, CBD is non-intoxicating. In the 28 states where medical marijuana is legal, CBD products are covered by those same medical marijuana legal protections.
In recent years, 16 states have passed CBD-only laws, which legalize the possession and use of CBD products for specific qualifying conditions—but not cannabis products containing higher levels of THC. Those CBD-only laws often limit the legal possession and use of CBD products to children with epilepsy, and some nerve and muscle afflictions.
Even in those states with CBD legal protections, however, the substance is considered federally illegal by the DEA.
Only six states—Idaho, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, Indiana, and West Virginia—still consider every part of the cannabis plant, including CBD, to be illegal.
Most states with CBD-only laws allow possession, but do not allow licensed dispensaries, home cultivation, or any other supply infrastructure. In other words, registered patients can have it and use it but can’t legally obtain it.
In Georgia, for example, the legislature passed a law in 2015 that made legal possession of up to 20 ounces of CBD for patients with qualifying conditions like seizure disorders and multiple sclerosis. The law does not, however, set up any supply infrastructure—there are no licensed dispensaries or producers. Recently, the Georgia legislature passed a compromise law that includes Alzheimer’s disease, AIDS, autism, epidermolysis bullosa, peripheral neuropathy, and Tourette’s syndrome in the list of diseases that can be treated by CBD—as long as that CBD oil has no more than 5 percent THC.


No Pings Yet